Navigating the Rise of Bacterial Pneumonia: Insights and Precautions
As winter’s chill sets in, health professionals and organizations brace for the annual uptick in respiratory illnesses, including pneumonia. This year, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have reported a noticeable increase in pneumonia diagnoses, especially among children—a trend that IBEC is closely monitoring.
Understanding Pneumonia:
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by various pathogens, including viruses and bacteria. Symptoms of pneumonia typically include a combination of coughing, fever, and difficulty breathing. The condition can be particularly severe in children and the elderly.
Recognizing Bacterial Pneumonia:
Bacterial pneumonia is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs that requires prompt attention. Being able to recognize the signs and symptoms is critical for early treatment and to prevent potential complications. Here are the key indicators to be aware of:
- High Fever: A sudden onset of high fever is often one of the first signs of bacterial pneumonia.
- Productive Cough: A cough that produces thick, greenish, or yellow phlegm can indicate bacterial pneumonia.
- Chest Pain: Sharp or stabbing chest pain that worsens with deep breaths or coughs is a symptom to watch for.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or rapid, shallow breaths may occur as the lungs struggle to breathe oxygen.
- Chills and Sweats: Severe chills and sweating, often accompanying fever, are common with bacterial pneumonia.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Feeling unusually tired or weak, even without significant exertion, can be a sign of pneumonia.
- Change in Mental Awareness: In older adults, confusion or changes in mental awareness can sometimes be the only sign.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Bacterial pneumonia can be confirmed through a full physical exam and examination, chest X-ray, and blood tests by a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are essential for recovery.
CDC’s Current Findings:
CDC has been monitoring increases in respiratory illness reported recently worldwide, including in China and several European countries.
The CDC’s surveillance has revealed that emergency department visits for pediatric pneumonia align with past years for children between 0 to 4 years old, with a slight increase in cases for children aged 5 to 17. These patterns are expected during the colder months when respiratory viruses are more prevalent.
National Weekly Percent of Emergency Department Visits for Pneumonia Among Patients Aged 0-17 Years
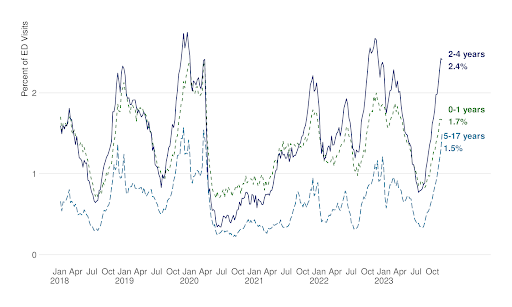
Includes the following diagnosis codes: J09.X1 Influenza due to identified novel influenza A virus with pneumonia; J10.0 Influenza due to other identified influenza virus with pneumonia; J11.0 Influenza due to unidentified influenza virus with pneumonia; J12 Viral pneumonia, not elsewhere classified; J13 Pneumonia due to Streptococcus pneumoniae; J14 Pneumonia due to Hemophilus influenzae; J15 Bacterial pneumonia, not elsewhere classified; J16 Pneumonia due to other infectious organisms, not elsewhere classified; J17 Pneumonia in diseases classified elsewhere; J18 Pneumonia, unspecified organism; J80 Acute respiratory distress syndrome; A48.1 Legionnaires’ disease; and J20.0 Acute bronchitis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Based on laboratory findings, these increases in pediatric pneumonia are not caused by a new virus or other pathogen. Instead, these increases are likely caused by viruses and bacteria we expect to see during the respiratory illness season.
The Importance of Being Informed About Bacterial Pneumonia
Staying informed about bacterial pneumonia is not just about knowledge but empowerment, prevention, and community health. Understanding this illness’s transmission, symptoms, and prevention strategies can significantly impact individual and public health outcomes. Here’s why being informed matters:
- Early Detection Saves Lives: Knowing the symptoms of bacterial pneumonia can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment, which is crucial for recovery, especially in vulnerable populations like children and the elderly.
- Prevention is Effective: Awareness of how bacterial pneumonia spreads empowers you to take effective preventive measures, such as vaccinations and good hygiene practices, which can greatly reduce disease incidence.
- Community Health: Knowledgeable individuals can contribute to the health of their communities by practicing and promoting behaviors that prevent the spread of pneumonia, such as advocating for vaccinations and proper ventilation in public spaces.
- Resource Utilization: Understanding the severity and impact of bacterial pneumonia ensures that community and healthcare resources are used wisely and where they are most needed.
- Reduces Healthcare Burden: By preventing illness and reducing disease severity through informed actions, we can help lessen the overall burden on healthcare systems, especially during peak respiratory illness seasons.
Preventative Measures:
The CDC emphasizes the importance of immunizations available for the major viral respiratory diseases that cause pneumonia, including influenza, COVID-19, and RSV. Vaccines against pneumococcal bacteria also help prevent the most common bacterial form of pneumonia.
Treatment and Testing:
Early detection through testing is crucial in managing pneumonia. Antiviral treatments for flu and COVID-19, alongside antibiotics for bacterial infections, can greatly reduce the severity of the disease.
Additional Protective Actions:
Beyond medical interventions, there are several ways to reduce the various risk factors of contracting or spreading pneumonia:
- Masking, especially in crowded indoor spaces.
- Physical distancing where possible.
- Regular hand washing with soap.
- Improving ventilation in indoor environments to reduce the concentration of airborne pathogens.
As the respiratory illness season intensifies, our collective efforts in vaccination, treatment, testing, and environmental safety can help mitigate the spread of pneumonia. We can protect ourselves and those around us with the right information and tools.
IBEC, in collaboration with Commit to C.A.R.E., stands ready to provide the tools and information needed to navigate this season safely. By leveraging risk assessment tools, enhancing indoor air quality, and adhering to recommended health practices, we can establish a strong defense against respiratory illnesses.
Commit to C.A.R.E.: Equipping You Against Bacterial Pneumonia
Commit to C.A.R.E. (C2C) empowers individuals and organizations with the tools and knowledge to combat bacterial pneumonia, a common yet serious lung infection. Our comprehensive approach to wellness and safety encompasses several key resources:
- Risk Assessment Tools: Understanding your risk is the first step to prevention. C2C’s risk assessment tools are designed to help you evaluate your environment and practices, pinpointing areas where improvements can be made to reduce the likelihood of infection. These tools consider factors such as air circulation, population density, and hygiene practices to provide a personalized risk profile.
- Indoor Air Quality Tools: The air we breathe indoors is crucial in spreading respiratory infections. Our indoor air quality tools can help you ensure your air is as clean and pathogen-free as possible. From advanced air purifiers to guidelines for effective ventilation systems, C2C provides various solutions to improve the air quality in homes, offices, and public spaces.
Improve Your Indoor Air Quality
- Access to Expertise: We understand that navigating health information can be overwhelming. That’s why we’ve made it easy to connect with experts. Whether you need advice on implementing risk reduction strategies or have questions about our tools, our team is here to support you.
- Community Support: At C2C, we believe in the power of community. we offer a space for individuals and organizations to share experiences, tips, and encouragement.
You can proactively protect yourself and others from bacterial pneumonia by leveraging these resources. Our commitment is in our name—C2C stands ready to help you Care, Assess, Remediate, and Educate.
Related Blogposts
How Climate Change is Propelling the Spread of Infectious Disease
By Stephane Bilodeau, Eng., Ph.D., FEC, Chief Science Officer at IBECClimate change is not only an ecological crisis; it fundamentally alters public health dynamics worldwide…
IBEC Statement on the Quarantine of Cargo Ship in Argentina Due to Suspected Mpox Case
The recent news regarding the quarantine of a cargo ship near Argentina’s Rosario Port due to a suspected case of mpox underscores the continued global…
Interdisciplinary Collaboration in Environmental Science: Pioneering Health Solutions with IBEC’s New CSO
The Integrated Bioscience and Built Environment Consortium (IBEC) proudly introduces its new Chief Scientific Officer (CSO), Stephane Bilodeau. Bringing over 25 years of diverse experience…
New COVID-19 Variant JN.1 Raises in the United States
JN.1 is a highly contagious, fast-spreading subvariant of omicron that has become the dominant strain in the country. According to data from the Centers for…
Pioneering Steps to Control Infectious Aerosols: Dr. Claire Bird Offers Expert Insight on ASHRAE’s New Draft Standard
As we navigate through the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic and other airborne diseases, there is a dire need to implement measures that will…
IBEC Takes the Lead in Developing a Framework for Reducing Indoor Pathogen Transmission
Dear IBEC Partners and Supporters, As we continue to navigate the ongoing threat of airborne pathogens transmission in our shared indoor communities, it’s more important…
New Commit To C.A.R.E. Resources Deliver Innovative Indoor Air Quality Solutions for Safer Workplaces
The Commit to C.A.R.E initiative The Integrated Bioscience and Built Environment Consortium (IBEC) and The American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA), two leading organizations committed to…
Staying Ahead of Severe GAS Infections and Other Secondary Bacterial Infections
Severe Group A Streptococcal (GAS) infections, including invasive disease (iGAS), can lead to life-threatening illness and death. CDC is looking into an increase in…
Industry Leader L’Oréal Pledges to Support Commit to C.A.R.E.
Industry Leader L’Oréal Pledges to Support Commit to C.A.R.E. With health experts warning of the triple threat of the continued spread of new COVID-19…
C.L.E.A.N. Lessons Learned: How to protect the healthcare system from current and future pandemics
The COVID-19 pandemic caught the world off guard. Health organizations all over the globe rushed into a quick response to protect people from the threat…